Tools for Risk Adjustment for Health Insurance

Introduction:
A mechanism called risk adjustment is used to make sure that insurers get paid enough to cover the population's medical expenses. Recent research has shown how important risk adjustment is for maintaining a competitive private health insurance market, preventing discrimination in insurer premiums, and designing benefit plans for people with serious health requirements. a statistical method that considers the insurance plan participants' underlying health status and health spending when analysing the outcomes or costs of their medical care. Today, a lot of healthcare software development services are available for help.
The purpose of risk adjustment is to make sure that insurers obtain the proper premium income or compensation to pay for the medical expenses of the enrolees they insure. Individuals cannot also be denied coverage according to their health status (known as guaranteed availability of coverage).
- Analytics for Medical Records: Although not all insurance plans employ data analytics to estimate medical costs, those that do frequently have the best risk management outcomes. This is because analytics enable the detection of patterns and trends in claims data that would otherwise be challenging. By using this data to create tailored, data-driven solutions, plan administrators can eliminate guesswork from risk management and identify potential issue areas before they go out of control. When it comes to combating fraud, these techniques are very beneficial. They can ensure that insurance companies are covering their fair share of medical expenses without taking on unnecessary liability by presenting convincing proof of fraud or misuse. We can use HL7 data integration services for help. Health Level Seven is the name of the standard for information transmission between medical information systems (HL7). It is widely utilised and includes information sharing across numerous functional domains. Healthcare interoperability is essential and hugely important.
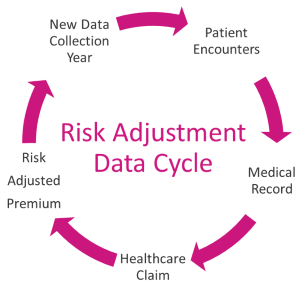
Risk Scoring: The risk score assigned to each patient indicates the likelihood that they will submit an insurance claim within a specific year. One's score and likelihood of filing a claim increase with the number of points they receive in a particular year. In order to prevent future expensive consequences, it is important to identify patients who are more likely than the average member to encounter higher health risks or more frequent health concerns. Plans often make use of this data to develop focused interventions aimed at raising patients' health literacy and enhancing general health outcomes. This kind of risk stratification can also be used to evaluate eligibility, which is crucial for people who are not qualified for government health insurance under the Affordable Care Act.
Some of the most often utilised methods:
- Risk scores,
- clinical risk scores,
- event histories,
- prescription pattern analyses,
- provider risk scores,
- external data providers including pharmacy and medical claims data.
Several tools exist that incorporate a variety of different data sources.
- Predictive Modelling: Predictive modelling is being used more frequently by insurance companies to produce insights for risk analysis. They employ big data and examine its potential for forecasting medical results. They start by looking at previous outcomes to evaluate if it's maximising their care/hospital resources, elevating patient satisfaction, and/or cutting expenses to improve patient outcomes. When a health plan starts using predictive modelling, they frequently begin with predictive analytics to gather and analyse historical and current data before moving on to prescriptive analytics to determine the most likely courses of action in order to drive the best outcomes possible based on that data. These technologies can help plan managers identify high-risk populations early so they can take action to avoid expensive health care.
- Analysis of the Event History (EHA): a method used to calculate the likelihood of future hospitalisations and visits by looking for trends in a member's health care (visits, procedures, and admissions). EHA is occasionally used to forecast the risk of developing chronic illnesses like diabetes or hypertension. Additionally, it can be used to determine which members are most likely to benefit from specific preventive treatments or may be at a higher risk of contracting a particular ailment.
- Health Risk Scores: Patient-level evaluation the likelihood that each patient will experience a specific condition within the following 12 months is determined by this form of clinical risk score, which is the most prevalent. Based on the patient's prior medical history, certain plans may also determine the likelihood that they would have a particular condition. Although the standards for determining patient risk differ from plan to plan, they often take into account elements including age, gender, pre-existing medical problems, and drug use. We can use EHR interoperability solutions for more help.
A "risk score" is given to a group of participants based on their medical background and present health. The likelihood that a person may experience one or more health issues within the upcoming year increases with an increasing risk score.
Conclusion:
The complicated nature of health care delivery and the numerous variables that could potentially affect each patient's health limit the efficacy of predictive modelling techniques, even if they have shown promise in some circumstances. Predictive analytics models must be created in collaboration with subject matter experts and user groups to ensure the proper level of clinical validity and utility in order to increase the effectiveness of patient care and decrease the incidence of avoidable complications and adverse events. System-level evaluation. The goal of system-level risk scoring is to identify clinical and demographic risk indicators that are shared by a group of patients with comparable illnesses or injuries. The possibility that patients in this group may encounter particular problems in the future can then be estimated using these risk variables.





